LeetCode in Kotlin
3604. Minimum Time to Reach Destination in Directed Graph
Medium
You are given an integer n and a directed graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. This is represented by a 2D array edges, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, starti, endi] indicates an edge from node ui to vi that can only be used at any integer time t such that starti <= t <= endi.
You start at node 0 at time 0.
In one unit of time, you can either:
- Wait at your current node without moving, or
- Travel along an outgoing edge from your current node if the current time
tsatisfiesstarti <= t <= endi.
Return the minimum time required to reach node n - 1. If it is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,0,1],[1,2,2,5]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
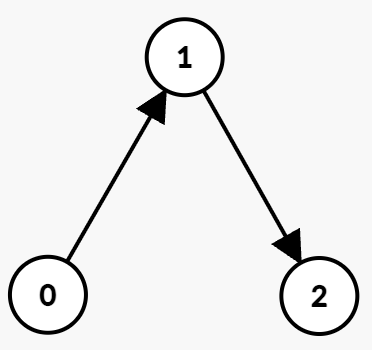
The optimal path is:
- At time
t = 0, take the edge(0 → 1)which is available from 0 to 1. You arrive at node 1 at timet = 1, then wait untilt = 2. - At time
t = `2`, take the edge(1 → 2)which is available from 2 to 5. You arrive at node 2 at time 3.
Hence, the minimum time to reach node 2 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,0,3],[1,3,7,8],[0,2,1,5],[2,3,4,7]]
Output: 5
Explanation:
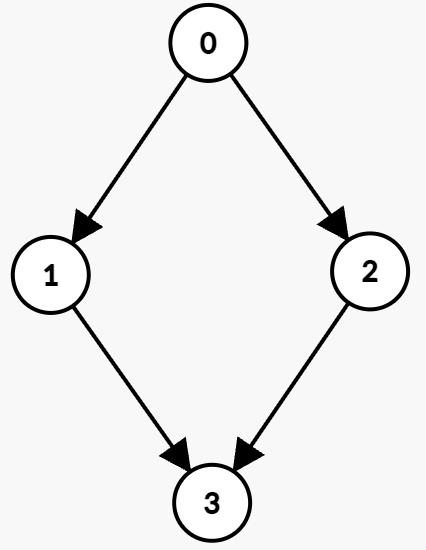
The optimal path is:
- Wait at node 0 until time
t = 1, then take the edge(0 → 2)which is available from 1 to 5. You arrive at node 2 att = 2. - Wait at node 2 until time
t = 4, then take the edge(2 → 3)which is available from 4 to 7. You arrive at node 3 att = 5.
Hence, the minimum time to reach node 3 is 5.
Example 3:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[1,0,1,3],[1,2,3,5]]
Output: -1
Explanation:
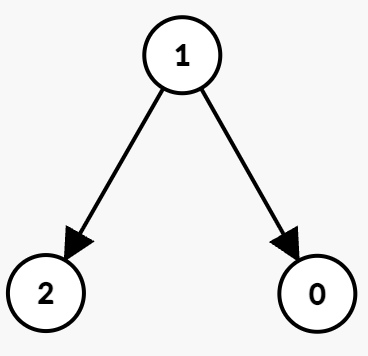
- Since there is no outgoing edge from node 0, it is impossible to reach node 2. Hence, the output is -1.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1050 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i] == [ui, vi, starti, endi]0 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi0 <= starti <= endi <= 109
Solution
import kotlin.math.max
class Solution {
fun minTime(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val head = IntArray(n)
val to = IntArray(edges.size)
val start = IntArray(edges.size)
val end = IntArray(edges.size)
val next = IntArray(edges.size)
head.fill(-1)
for (i in edges.indices) {
val u = edges[i][0]
to[i] = edges[i][1]
start[i] = edges[i][2]
end[i] = edges[i][3]
next[i] = head[u]
head[u] = i
}
val heap = IntArray(n)
val time = IntArray(n)
val pos = IntArray(n)
val visited = BooleanArray(n)
var size = 0
for (i in 0..<n) {
time[i] = INF
pos[i] = -1
}
time[0] = 0
heap[size] = 0
pos[0] = 0
size++
while (size > 0) {
val u = heap[0]
heap[0] = heap[--size]
pos[heap[0]] = 0
heapifyDown(heap, time, pos, size, 0)
if (visited[u]) {
continue
}
visited[u] = true
if (u == n - 1) {
return time[u]
}
var e = head[u]
while (e != -1) {
val v = to[e]
val t0 = time[u]
if (t0 > end[e]) {
e = next[e]
continue
}
val arrival = max(t0, start[e]) + 1
if (arrival < time[v]) {
time[v] = arrival
if (pos[v] == -1) {
heap[size] = v
pos[v] = size
heapifyUp(heap, time, pos, size)
size++
} else {
heapifyUp(heap, time, pos, pos[v])
}
}
e = next[e]
}
}
return -1
}
private fun heapifyUp(heap: IntArray, time: IntArray, pos: IntArray, i: Int) {
var i = i
while (i > 0) {
val p = (i - 1) / 2
if (time[heap[p]] <= time[heap[i]]) {
break
}
swap(heap, pos, i, p)
i = p
}
}
private fun heapifyDown(heap: IntArray, time: IntArray, pos: IntArray, size: Int, i: Int) {
var i = i
while (2 * i + 1 < size) {
var j = 2 * i + 1
if (j + 1 < size && time[heap[j + 1]] < time[heap[j]]) {
j++
}
if (time[heap[i]] <= time[heap[j]]) {
break
}
swap(heap, pos, i, j)
i = j
}
}
private fun swap(heap: IntArray, pos: IntArray, i: Int, j: Int) {
val tmp = heap[i]
heap[i] = heap[j]
heap[j] = tmp
pos[heap[i]] = i
pos[heap[j]] = j
}
companion object {
private const val INF = Int.Companion.MAX_VALUE
}
}

