LeetCode in Kotlin
3544. Subtree Inversion Sum
Hard
You are given an undirected tree rooted at node 0, with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The tree is represented by a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates an edge between nodes ui and vi.
You are also given an integer array nums of length n, where nums[i] represents the value at node i, and an integer k.
You may perform inversion operations on a subset of nodes subject to the following rules:
-
Subtree Inversion Operation:
- When you invert a node, every value in the subtree rooted at that node is multiplied by -1.
-
Distance Constraint on Inversions:
-
You may only invert a node if it is “sufficiently far” from any other inverted node.
-
Specifically, if you invert two nodes
aandbsuch that one is an ancestor of the other (i.e., ifLCA(a, b) = aorLCA(a, b) = b), then the distance (the number of edges on the unique path between them) must be at leastk.
-
Return the maximum possible sum of the tree’s node values after applying inversion operations.
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]], nums = [4,-8,-6,3,7,-2,5], k = 2
Output: 27
Explanation:
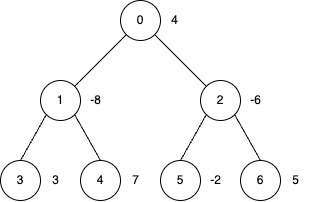
- Apply inversion operations at nodes 0, 3, 4 and 6.
- The final
numsarray is[-4, 8, 6, 3, 7, 2, 5], and the total sum is 27.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]], nums = [-1,3,-2,4,-5], k = 2
Output: 9
Explanation:
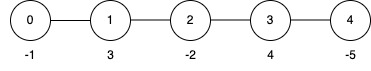
- Apply the inversion operation at node 4.
- The final
numsarray becomes[-1, 3, -2, 4, 5], and the total sum is 9.
Example 3:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], nums = [0,-1,-2], k = 3
Output: 3
Explanation:
Apply inversion operations at nodes 1 and 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i] = [ui, vi]0 <= ui, vi < nnums.length == n-5 * 104 <= nums[i] <= 5 * 1041 <= k <= 50- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
import kotlin.math.max
import kotlin.math.min
class Solution {
private lateinit var totalSum: LongArray
private lateinit var nums: IntArray
private lateinit var nei: MutableList<MutableList<Int>>
private var k = 0
private fun getTotalSum(p: Int, cur: Int): Long {
var res = nums[cur].toLong()
for (c in nei[cur]) {
if (c == p) {
continue
}
res += getTotalSum(cur, c)
}
totalSum[cur] = res
return res
}
private fun add(a: Array<LongArray>, b: Array<LongArray>) {
for (i in a.indices) {
for (j in a[0].indices) {
a[i][j] += b[i][j]
}
}
}
private fun getMaxInc(p: Int, cur: Int): Array<LongArray> {
val ret = Array<LongArray>(3) { LongArray(k) }
for (c in nei[cur]) {
if (c == p) {
continue
}
add(ret, getMaxInc(cur, c))
}
val maxCandWithoutInv = nums[cur] + ret[2][0]
val maxCandWithInv = -(totalSum[cur] - ret[0][k - 1]) - ret[1][k - 1]
val minCandWithoutInv = nums[cur] + ret[1][0]
val minCandWithInv = -(totalSum[cur] - ret[0][k - 1]) - ret[2][k - 1]
val res = Array<LongArray>(3) { LongArray(k) }
for (i in 0..<k - 1) {
res[0][i + 1] = ret[0][i]
res[1][i + 1] = ret[1][i]
res[2][i + 1] = ret[2][i]
}
res[0][0] = totalSum[cur]
res[1][0] = min(
min(maxCandWithoutInv, maxCandWithInv),
min(minCandWithoutInv, minCandWithInv),
)
res[2][0] = max(
max(maxCandWithoutInv, maxCandWithInv),
max(minCandWithoutInv, minCandWithInv),
)
return res
}
fun subtreeInversionSum(edges: Array<IntArray>, nums: IntArray, k: Int): Long {
totalSum = LongArray(nums.size)
this.nums = nums
nei = ArrayList<MutableList<Int>>()
this.k = k
for (i in nums.indices) {
nei.add(ArrayList<Int>())
}
for (e in edges) {
nei[e[0]].add(e[1])
nei[e[1]].add(e[0])
}
getTotalSum(-1, 0)
val res = getMaxInc(-1, 0)
return res[2][0]
}
}

