LeetCode in Kotlin
3534. Path Existence Queries in a Graph II
Hard
You are given an integer n representing the number of nodes in a graph, labeled from 0 to n - 1.
You are also given an integer array nums of length n and an integer maxDiff.
An undirected edge exists between nodes i and j if the absolute difference between nums[i] and nums[j] is at most maxDiff (i.e., |nums[i] - nums[j]| <= maxDiff).
You are also given a 2D integer array queries. For each queries[i] = [ui, vi], find the minimum distance between nodes ui and vi. If no path exists between the two nodes, return -1 for that query.
Return an array answer, where answer[i] is the result of the ith query.
Note: The edges between the nodes are unweighted.
Example 1:
Input: n = 5, nums = [1,8,3,4,2], maxDiff = 3, queries = [[0,3],[2,4]]
Output: [1,1]
Explanation:
The resulting graph is:
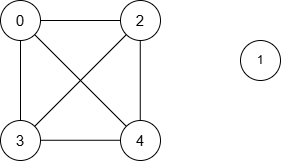
| Query | Shortest Path | Minimum Distance |
|---|---|---|
| [0, 3] | 0 → 3 | 1 |
| [2, 4] | 2 → 4 | 1 |
Thus, the output is [1, 1].
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, nums = [5,3,1,9,10], maxDiff = 2, queries = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[4,3]]
Output: [1,2,-1,1]
Explanation:
The resulting graph is:
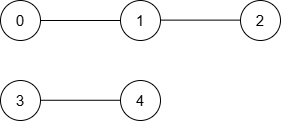
Here is the equivalent Markdown for the given HTML table:
| Query | Shortest Path | Minimum Distance |
|---|---|---|
| [0, 1] | 0 → 1 | 1 |
| [0, 2] | 0 → 1 → 2 | 2 |
| [2, 3] | None | -1 |
| [4, 3] | 3 → 4 | 1 |
Thus, the output is [1, 2, -1, 1].
Example 3:
Input: n = 3, nums = [3,6,1], maxDiff = 1, queries = [[0,0],[0,1],[1,2]]
Output: [0,-1,-1]
Explanation:
There are no edges between any two nodes because:
- Nodes 0 and 1:
|nums[0] - nums[1]| = |3 - 6| = 3 > 1 - Nodes 0 and 2:
|nums[0] - nums[2]| = |3 - 1| = 2 > 1 - Nodes 1 and 2:
|nums[1] - nums[2]| = |6 - 1| = 5 > 1
Thus, no node can reach any other node, and the output is [0, -1, -1].
Constraints:
1 <= n == nums.length <= 1050 <= nums[i] <= 1050 <= maxDiff <= 1051 <= queries.length <= 105queries[i] == [ui, vi]0 <= ui, vi < n
Solution
import kotlin.math.abs
class Solution {
fun pathExistenceQueries(n: Int, nums: IntArray, maxDiff: Int, queries: Array<IntArray>): IntArray {
val position = IntArray(n)
val values = IntArray(n)
val sortedIndices = Array(n) { i -> i }
sortedIndices.sortWith { a: Int, b: Int -> nums[a].compareTo(nums[b]) }
for (i in 0..<n) {
position[sortedIndices[i]] = i
values[i] = nums[sortedIndices[i]]
}
val reachableIndex = IntArray(n)
var j = 0
for (i in 0..<n) {
if (j < i) {
j = i
}
while (j + 1 < n && values[j + 1] - values[i] <= maxDiff) {
j++
}
reachableIndex[i] = j
}
var maxLog = 1
while ((1 shl maxLog) < n) {
maxLog++
}
val upTable = Array(maxLog) { IntArray(n) }
upTable[0] = reachableIndex.clone()
for (k in 1..<maxLog) {
for (i in 0..<n) {
upTable[k][i] = upTable[k - 1][upTable[k - 1][i]]
}
}
val results = IntArray(queries.size)
for (idx in queries.indices) {
val start = queries[idx][0]
val end = queries[idx][1]
if (start == end) {
results[idx] = 0
continue
}
var startPos = position[start]
var endPos = position[end]
if (startPos > endPos) {
val temp = startPos
startPos = endPos
endPos = temp
}
if (abs(nums[start] - nums[end]) <= maxDiff) {
results[idx] = 1
continue
}
if (reachableIndex[startPos] < endPos) {
var current = startPos
var jumpCount = 0
for (k in maxLog - 1 downTo 0) {
if (upTable[k][current] < endPos) {
if (upTable[k][current] == current) {
break
}
current = upTable[k][current]
jumpCount += 1 shl k
}
}
if (reachableIndex[current] >= endPos) {
results[idx] = jumpCount + 1
} else {
results[idx] = -1
}
} else {
results[idx] = 1
}
}
return results
}
}

