LeetCode in Kotlin
3515. Shortest Path in a Weighted Tree
Hard
You are given an integer n and an undirected, weighted tree rooted at node 1 with n nodes numbered from 1 to n. This is represented by a 2D array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates an undirected edge from node ui to vi with weight wi.
You are also given a 2D integer array queries of length q, where each queries[i] is either:
[1, u, v, w']– Update the weight of the edge between nodesuandvtow', where(u, v)is guaranteed to be an edge present inedges.[2, x]– Compute the shortest path distance from the root node 1 to nodex.
Return an integer array answer, where answer[i] is the shortest path distance from node 1 to x for the ith query of [2, x].
Example 1:
Input: n = 2, edges = [[1,2,7]], queries = [[2,2],[1,1,2,4],[2,2]]
Output: [7,4]
Explanation:
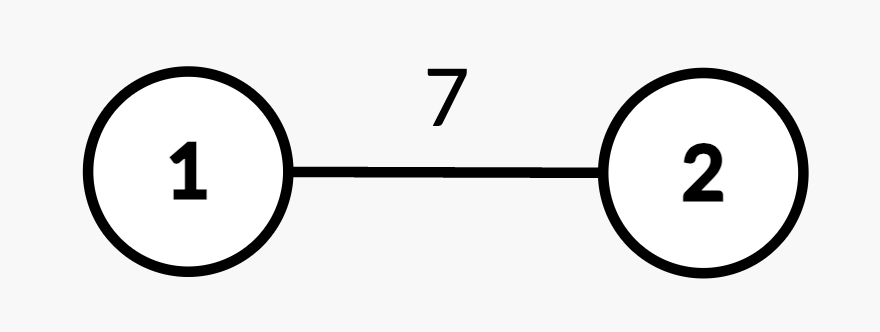
- Query
[2,2]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 7. - Query
[1,1,2,4]: The weight of edge(1,2)changes from 7 to 4. - Query
[2,2]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 4.
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[1,2,2],[1,3,4]], queries = [[2,1],[2,3],[1,1,3,7],[2,2],[2,3]]
Output: [0,4,2,7]
Explanation:
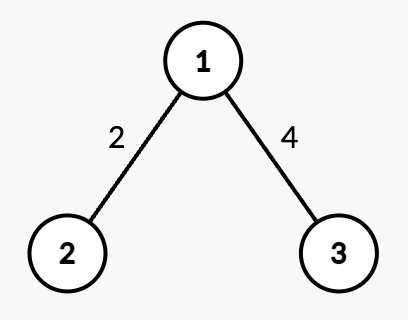
- Query
[2,1]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 1 is 0. - Query
[2,3]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 is 4. - Query
[1,1,3,7]: The weight of edge(1,3)changes from 4 to 7. - Query
[2,2]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 2. - Query
[2,3]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 is 7.
Example 3:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,2,2],[2,3,1],[3,4,5]], queries = [[2,4],[2,3],[1,2,3,3],[2,2],[2,3]]
Output: [8,3,2,5]
Explanation:
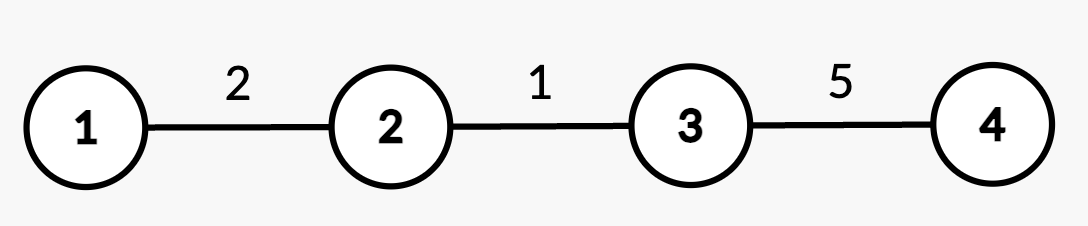
- Query
[2,4]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 4 consists of edges(1,2),(2,3), and(3,4)with weights2 + 1 + 5 = 8. - Query
[2,3]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 consists of edges(1,2)and(2,3)with weights2 + 1 = 3. - Query
[1,2,3,3]: The weight of edge(2,3)changes from 1 to 3. - Query
[2,2]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 2. - Query
[2,3]: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 consists of edges(1,2)and(2,3)with updated weights2 + 3 = 5.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i] == [ui, vi, wi]1 <= ui, vi <= n1 <= wi <= 104- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree. 1 <= queries.length == q <= 105queries[i].length == 2or4queries[i] == [1, u, v, w']or,queries[i] == [2, x]1 <= u, v, x <= n(u, v)is always an edge fromedges.1 <= w' <= 104
Solution
class Solution {
fun treeQueries(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>, queries: Array<IntArray>): IntArray {
// store the queries input midway as requested
val jalkimoren = queries
// build adjacency list with edge‐indices
val adj: Array<MutableList<Edge>> = Array(n + 1) { ArrayList() }
for (i in 0..<n - 1) {
val u = edges[i][0]
val v = edges[i][1]
val w = edges[i][2]
adj[u].add(Edge(v, w, i))
adj[v].add(Edge(u, w, i))
}
// parent, Euler‐tour times, depth‐sum, and mapping node→edge‐index
val parent = IntArray(n + 1)
val tin = IntArray(n + 1)
val tout = IntArray(n + 1)
val depthSum = IntArray(n + 1)
val edgeIndexForNode = IntArray(n + 1)
val weights = IntArray(n - 1)
for (i in 0..<n - 1) {
weights[i] = edges[i][2]
}
// iterative DFS to compute tin/tout, parent[], depthSum[], edgeIndexForNode[]
var time = 0
val stack = IntArray(n)
val ptr = IntArray(n + 1)
var sp = 0
stack[sp++] = 1
while (sp > 0) {
val u = stack[sp - 1]
if (ptr[u] == 0) {
tin[u] = ++time
}
if (ptr[u] < adj[u].size) {
val e = adj[u][ptr[u]++]
val v = e.to
if (v == parent[u]) {
continue
}
parent[v] = u
depthSum[v] = depthSum[u] + e.w
edgeIndexForNode[v] = e.idx
stack[sp++] = v
} else {
tout[u] = time
sp--
}
}
// Fenwick tree for range‐add / point‐query on Euler‐tour array
val bit = Fenwick(n + 2)
val answers: MutableList<Int> = ArrayList<Int>()
// process queries
for (q in jalkimoren) {
if (q[0] == 1) {
// update edge weight
val u = q[1]
val v = q[2]
val newW = q[3]
val child = if (parent[u] == v) u else v
val idx = edgeIndexForNode[child]
val delta = newW - weights[idx]
if (delta != 0) {
weights[idx] = newW
bit.rangeAdd(tin[child], tout[child], delta)
}
} else {
// query root→x distance
val x = q[1]
answers.add(depthSum[x] + bit.pointQuery(tin[x]))
}
}
// pack results into array
val m = answers.size
val ansArr = IntArray(m)
for (i in 0..<m) {
ansArr[i] = answers[i]
}
return ansArr
}
private class Edge(var to: Int, var w: Int, var idx: Int)
private class Fenwick(var n: Int) {
var f: IntArray = IntArray(n)
fun update(i: Int, v: Int) {
var i = i
while (i < n) {
f[i] += v
i += i and -i
}
}
fun rangeAdd(l: Int, r: Int, v: Int) {
update(l, v)
update(r + 1, -v)
}
fun pointQuery(i: Int): Int {
var i = i
var s = 0
while (i > 0) {
s += f[i]
i -= i and -i
}
return s
}
}
}

