LeetCode in Kotlin
3425. Longest Special Path
Hard
You are given an undirected tree rooted at node 0 with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1, represented by a 2D array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, lengthi] indicates an edge between nodes ui and vi with length lengthi. You are also given an integer array nums, where nums[i] represents the value at node i.
A special path is defined as a downward path from an ancestor node to a descendant node such that all the values of the nodes in that path are unique.
Note that a path may start and end at the same node.
Return an array result of size 2, where result[0] is the length of the longest special path, and result[1] is the minimum number of nodes in all possible longest special paths.
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,5],[1,4,4],[2,5,6]], nums = [2,1,2,1,3,1]
Output: [6,2]
Explanation:
In the image below, nodes are colored by their corresponding values in nums
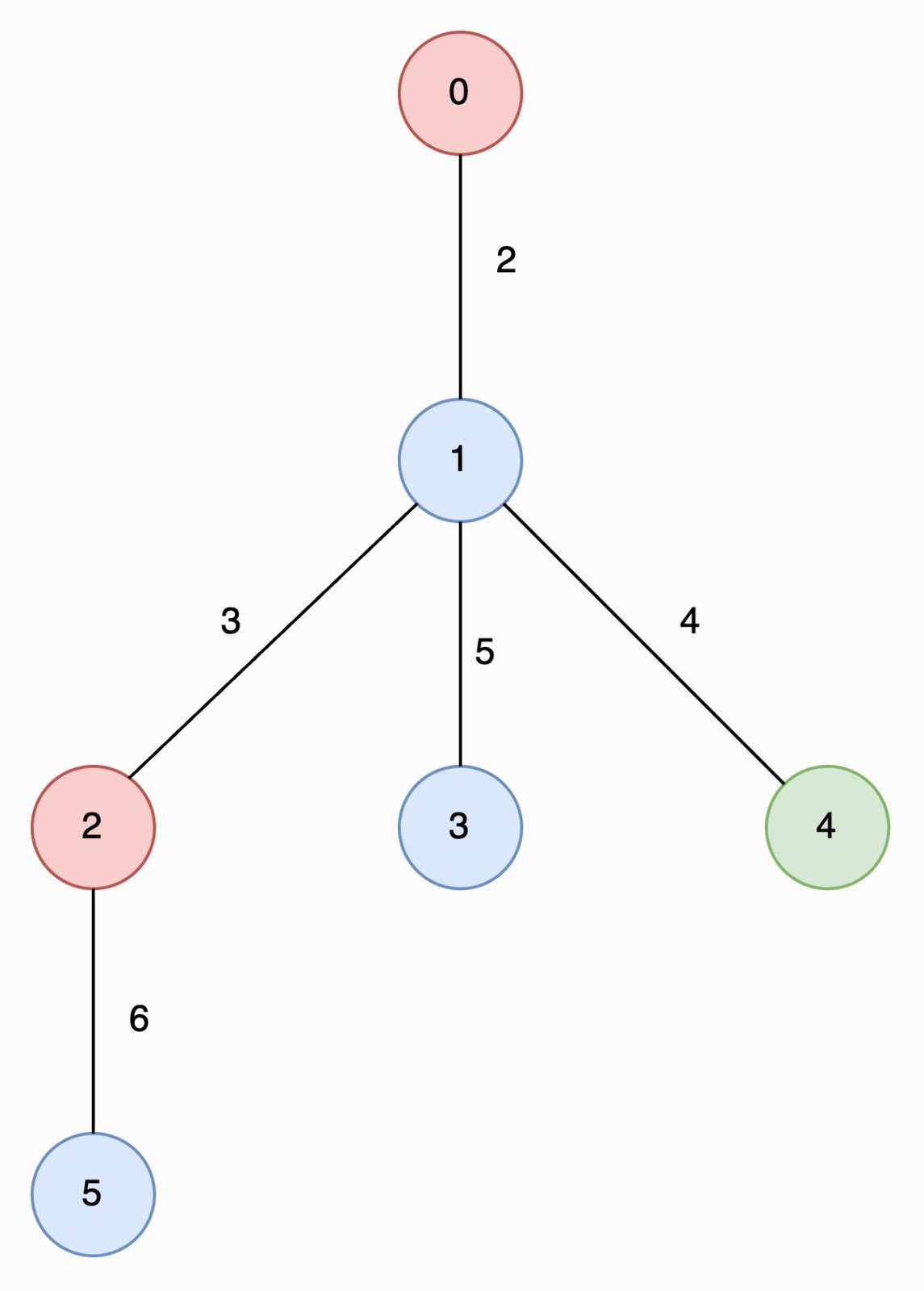
The longest special paths are 2 -> 5 and 0 -> 1 -> 4, both having a length of 6. The minimum number of nodes across all longest special paths is 2.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[1,0,8]], nums = [2,2]
Output: [0,1]
Explanation:
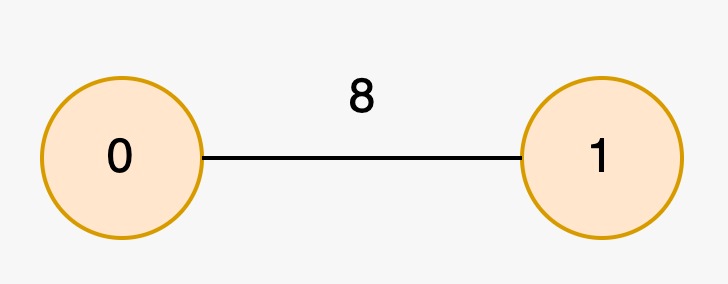
The longest special paths are 0 and 1, both having a length of 0. The minimum number of nodes across all longest special paths is 1.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi < n1 <= lengthi <= 103nums.length == n0 <= nums[i] <= 5 * 104- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
import kotlin.math.max
@Suppress("kotlin:S107")
class Solution {
fun longestSpecialPath(edges: Array<IntArray>, nums: IntArray): IntArray {
val n = edges.size + 1
var max = 0
val adj: Array<MutableList<IntArray>> = Array(n) { ArrayList<IntArray>() }
for (i in 0..<n) {
adj[i] = ArrayList<IntArray>()
max = max(nums[i], max)
}
for (e in edges) {
adj[e[0]].add(intArrayOf(e[1], e[2]))
adj[e[1]].add(intArrayOf(e[0], e[2]))
}
val dist = IntArray(n)
val res = intArrayOf(0, Int.Companion.MAX_VALUE)
val st = IntArray(n + 1)
val seen = arrayOfNulls<Int>(max + 1)
dfs(adj, nums, res, dist, seen, st, 0, -1, 0, 0)
return res
}
private fun dfs(
adj: Array<MutableList<IntArray>>,
nums: IntArray,
res: IntArray,
dist: IntArray,
seen: Array<Int?>,
st: IntArray,
node: Int,
parent: Int,
start: Int,
pos: Int,
) {
var start = start
val last = seen[nums[node]]
if (last != null && last >= start) {
start = last + 1
}
seen[nums[node]] = pos
st[pos] = node
val len = dist[node] - dist[st[start]]
val sz = pos - start + 1
if (res[0] < len || res[0] == len && res[1] > sz) {
res[0] = len
res[1] = sz
}
for (neighbor in adj[node]) {
if (neighbor[0] == parent) {
continue
}
dist[neighbor[0]] = dist[node] + neighbor[1]
dfs(adj, nums, res, dist, seen, st, neighbor[0], node, start, pos + 1)
}
seen[nums[node]] = last
}
}

