LeetCode in Kotlin
3327. Check if DFS Strings Are Palindromes
Hard
You are given a tree rooted at node 0, consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The tree is represented by an array parent of size n, where parent[i] is the parent of node i. Since node 0 is the root, parent[0] == -1.
You are also given a string s of length n, where s[i] is the character assigned to node i.
Consider an empty string dfsStr, and define a recursive function dfs(int x) that takes a node x as a parameter and performs the following steps in order:
- Iterate over each child
yofxin increasing order of their numbers, and calldfs(y). - Add the character
s[x]to the end of the stringdfsStr.
Note that dfsStr is shared across all recursive calls of dfs.
You need to find a boolean array answer of size n, where for each index i from 0 to n - 1, you do the following:
- Empty the string
dfsStrand calldfs(i). - If the resulting string
dfsStris a palindrome, then setanswer[i]totrue. Otherwise, setanswer[i]tofalse.
Return the array answer.
A palindrome is a string that reads the same forward and backward.
Example 1:
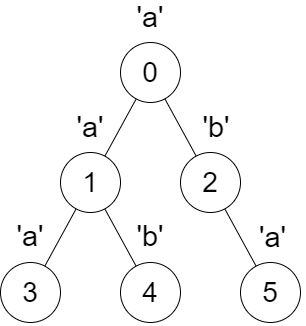
Input: parent = [-1,0,0,1,1,2], s = “aababa”
Output: [true,true,false,true,true,true]
Explanation:
- Calling
dfs(0)results in the stringdfsStr = "abaaba", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(1)results in the stringdfsStr = "aba", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(2)results in the stringdfsStr = "ab", which is not a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(3)results in the stringdfsStr = "a", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(4)results in the stringdfsStr = "b", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(5)results in the stringdfsStr = "a", which is a palindrome.
Example 2:
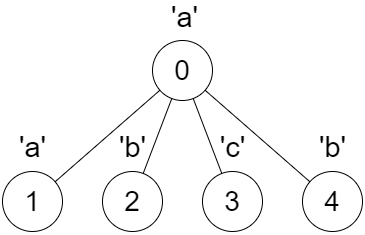
Input: parent = [-1,0,0,0,0], s = “aabcb”
Output: [true,true,true,true,true]
Explanation:
Every call on dfs(x) results in a palindrome string.
Constraints:
n == parent.length == s.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= parent[i] <= n - 1for alli >= 1.parent[0] == -1parentrepresents a valid tree.sconsists only of lowercase English letters.
Solution
import kotlin.math.min
class Solution {
private var time = 0
private lateinit var cs: ByteArray
private lateinit var graph: Array<IntArray?>
fun findAnswer(parent: IntArray, s: String): BooleanArray {
val n = s.length
cs = s.toByteArray()
graph = arrayOfNulls<IntArray>(n)
val childCount = IntArray(n)
for (i in 1..<n) {
childCount[parent[i]]++
}
for (i in 0..<n) {
graph[i] = IntArray(childCount[i])
childCount[i] = 0
}
for (i in 1..<n) {
graph[parent[i]]!![childCount[parent[i]]++] = i
}
val dfsStr = ByteArray(n)
val start = IntArray(n)
val end = IntArray(n)
dfs(0, dfsStr, start, end)
val lens = getRadius(dfsStr)
val ans = BooleanArray(n)
for (i in 0..<n) {
val l = start[i]
val r = end[i]
val center = l + r + 2
ans[i] = lens[center] >= r - l + 1
}
return ans
}
private fun dfs(u: Int, dfsStr: ByteArray, start: IntArray, end: IntArray) {
start[u] = time
for (v in graph[u]!!) {
dfs(v, dfsStr, start, end)
}
dfsStr[time] = cs[u]
end[u] = time++
}
private fun getRadius(cs: ByteArray): IntArray {
val n = cs.size
val t = ByteArray(2 * n + 3)
var m = 0
t[m++] = '@'.code.toByte()
t[m++] = '#'.code.toByte()
for (c in cs) {
t[m++] = c
t[m++] = '#'.code.toByte()
}
t[m++] = '$'.code.toByte()
val lens = IntArray(m)
var center = 0
var right = 0
for (i in 2..<m - 2) {
var len = 0
if (i < right) {
len = min(lens[2 * center - i], right - i)
}
while (t[i + len + 1] == t[i - len - 1]) {
len++
}
if (right < i + len) {
right = i + len
center = i
}
lens[i] = len
}
return lens
}
}

