LeetCode in Kotlin
3283. Maximum Number of Moves to Kill All Pawns
Hard
There is a 50 x 50 chessboard with one knight and some pawns on it. You are given two integers kx and ky where (kx, ky) denotes the position of the knight, and a 2D array positions where positions[i] = [xi, yi] denotes the position of the pawns on the chessboard.
Alice and Bob play a turn-based game, where Alice goes first. In each player’s turn:
- The player selects a pawn that still exists on the board and captures it with the knight in the fewest possible moves. Note that the player can select any pawn, it might not be one that can be captured in the least number of moves.
- In the process of capturing the selected pawn, the knight may pass other pawns without capturing them. Only the selected pawn can be captured in this turn.
Alice is trying to maximize the sum of the number of moves made by both players until there are no more pawns on the board, whereas Bob tries to minimize them.
Return the maximum total number of moves made during the game that Alice can achieve, assuming both players play optimally.
Note that in one move, a chess knight has eight possible positions it can move to, as illustrated below. Each move is two cells in a cardinal direction, then one cell in an orthogonal direction.
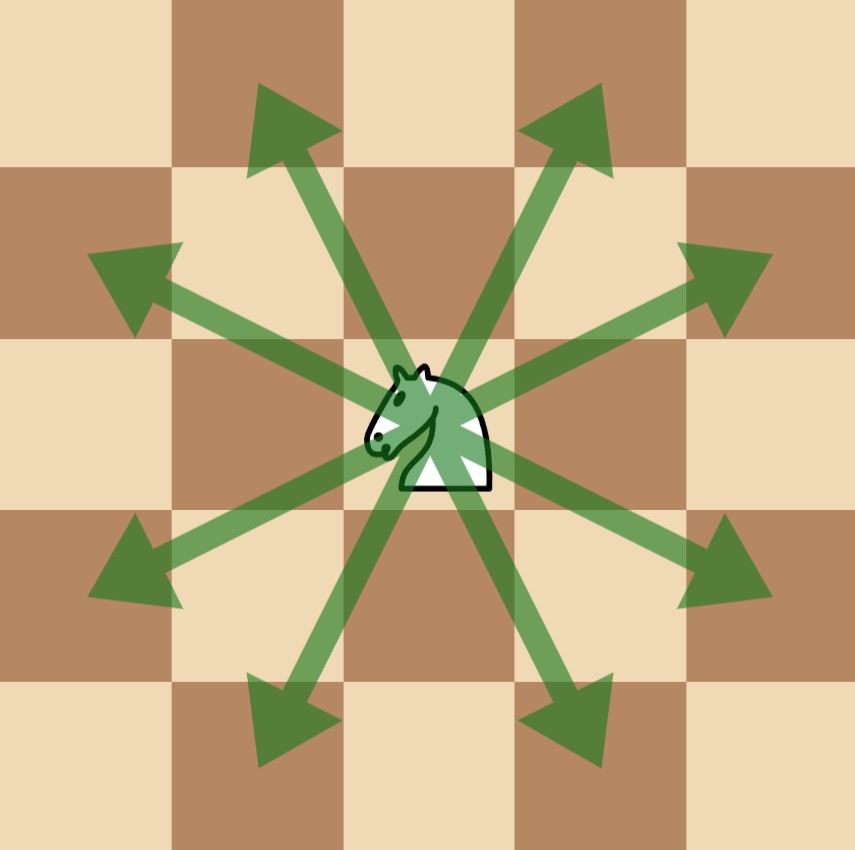

Example 1:
Input: kx = 1, ky = 1, positions = [[0,0]]
Output: 4
Explanation:
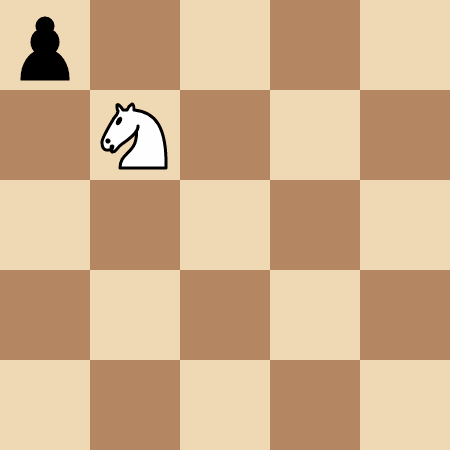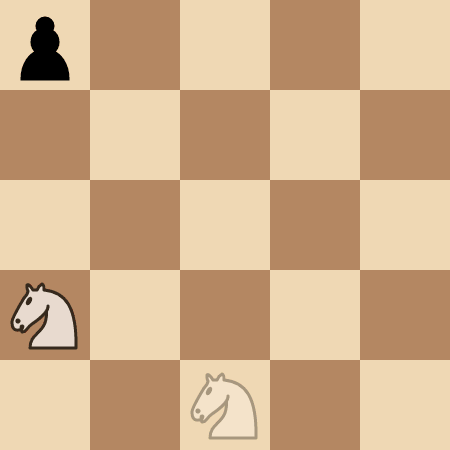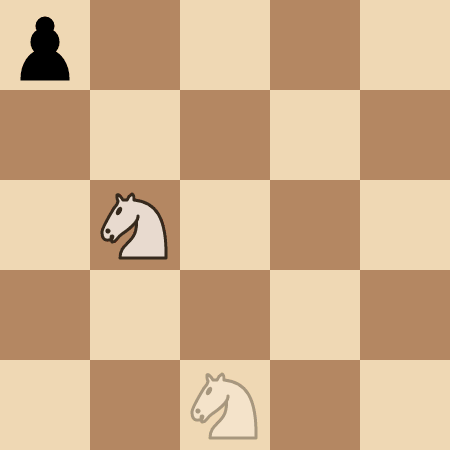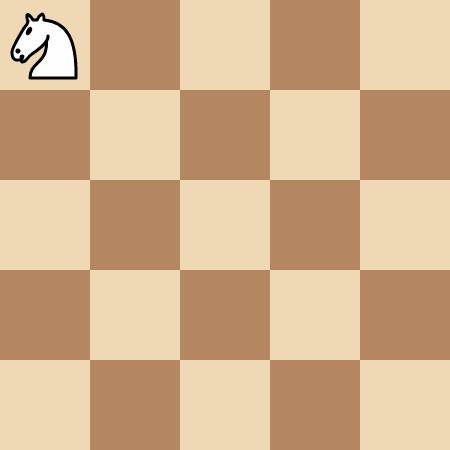
The knight takes 4 moves to reach the pawn at (0, 0).
Example 2:
Input: kx = 0, ky = 2, positions = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]]
Output: 8
Explanation:
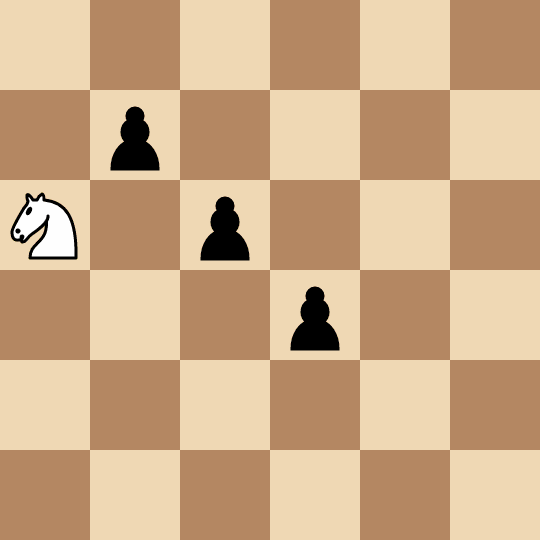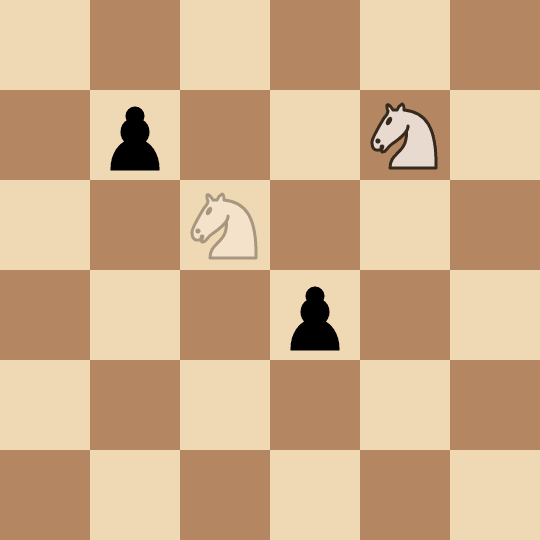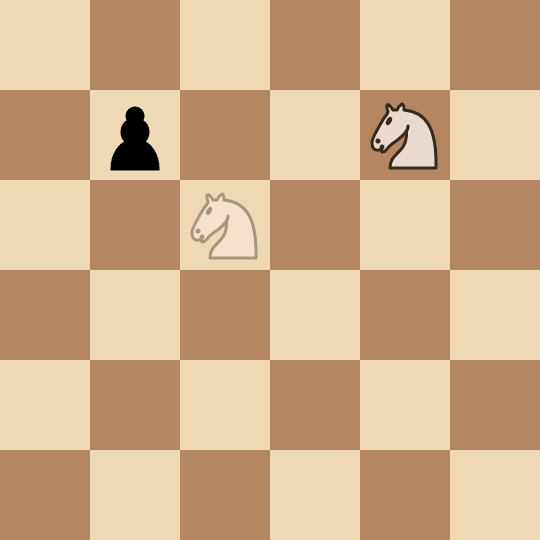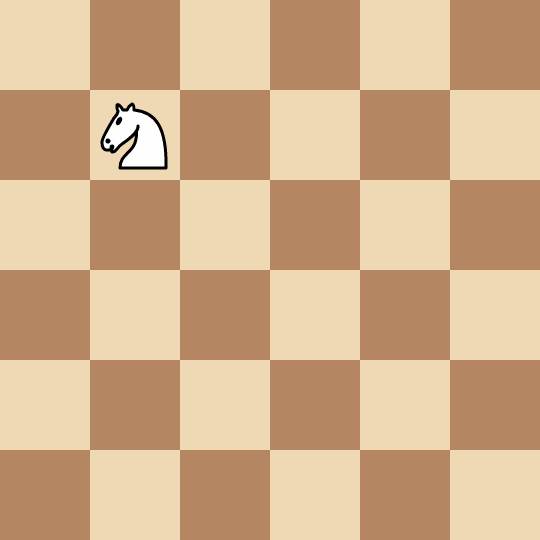
- Alice picks the pawn at
(2, 2)and captures it in two moves:(0, 2) -> (1, 4) -> (2, 2). - Bob picks the pawn at
(3, 3)and captures it in two moves:(2, 2) -> (4, 1) -> (3, 3). - Alice picks the pawn at
(1, 1)and captures it in four moves:(3, 3) -> (4, 1) -> (2, 2) -> (0, 3) -> (1, 1).
Example 3:
Input: kx = 0, ky = 0, positions = [[1,2],[2,4]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- Alice picks the pawn at
(2, 4)and captures it in two moves:(0, 0) -> (1, 2) -> (2, 4). Note that the pawn at(1, 2)is not captured. - Bob picks the pawn at
(1, 2)and captures it in one move:(2, 4) -> (1, 2).
Constraints:
0 <= kx, ky <= 491 <= positions.length <= 15positions[i].length == 20 <= positions[i][0], positions[i][1] <= 49- All
positions[i]are unique. - The input is generated such that
positions[i] != [kx, ky]for all0 <= i < positions.length.
Solution
import kotlin.math.max
import kotlin.math.min
class Solution {
private fun initializePositions(positions: Array<IntArray>, pos: Array<IntArray>, kx: Int, ky: Int) {
val n = positions.size
for (i in 0..<n) {
val x = positions[i][0]
val y = positions[i][1]
pos[x][y] = i
}
pos[kx][ky] = n
}
private fun calculateDistances(positions: Array<IntArray>, pos: Array<IntArray>, distances: Array<IntArray>) {
val n = positions.size
for (i in 0..<n) {
var count = n - i
val visited = Array<BooleanArray>(50) { BooleanArray(50) }
visited[positions[i][0]][positions[i][1]] = true
val que: ArrayDeque<IntArray> = ArrayDeque()
que.add(intArrayOf(positions[i][0], positions[i][1]))
var steps = 1
while (que.isNotEmpty() && count > 0) {
var size = que.size
while (size-- > 0) {
val cur = que.removeFirst()
val x = cur[0]
val y = cur[1]
for (d in DIRECTIONS) {
val nx = x + d[0]
val ny = y + d[1]
if (0 <= nx && nx < 50 && 0 <= ny && ny < 50 && !visited[nx][ny]) {
que.add(intArrayOf(nx, ny))
visited[nx][ny] = true
val j = pos[nx][ny]
if (j > i) {
distances[j][i] = steps
distances[i][j] = distances[j][i]
if (--count == 0) {
break
}
}
}
}
if (count == 0) {
break
}
}
steps++
}
}
}
private fun calculateDP(n: Int, distances: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = (1 shl n) - 1
val dp = Array<IntArray>(1 shl n) { IntArray(n + 1) }
for (mask in 1..<(1 shl n)) {
val isEven = (Integer.bitCount(m xor mask)) % 2 == 0
for (i in 0..n) {
var result = 0
if (isEven) {
for (j in 0..<n) {
if ((mask and (1 shl j)) > 0) {
result = max(
result,
dp[mask xor (1 shl j)][j] + distances[i][j],
)
}
}
} else {
result = Int.Companion.MAX_VALUE
for (j in 0..<n) {
if ((mask and (1 shl j)) > 0) {
result = min(
result,
dp[mask xor (1 shl j)][j] + distances[i][j],
)
}
}
}
dp[mask][i] = result
}
}
return dp[m][n]
}
fun maxMoves(kx: Int, ky: Int, positions: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val n = positions.size
val pos = Array<IntArray>(50) { IntArray(50) }
initializePositions(positions, pos, kx, ky)
val distances = Array<IntArray>(n + 1) { IntArray(n + 1) }
calculateDistances(positions, pos, distances)
return calculateDP(n, distances)
}
companion object {
private val DIRECTIONS = arrayOf<IntArray>(
intArrayOf(2, 1),
intArrayOf(1, 2),
intArrayOf(-1, 2),
intArrayOf(-2, 1),
intArrayOf(-2, -1),
intArrayOf(-1, -2),
intArrayOf(1, -2),
intArrayOf(2, -1),
)
}
}

