LeetCode in Kotlin
3242. Design Neighbor Sum Service
Easy
You are given a n x n 2D array grid containing distinct elements in the range [0, n2 - 1].
Implement the neighborSum class:
neighborSum(int [][]grid)initializes the object.int adjacentSum(int value)returns the sum of elements which are adjacent neighbors ofvalue, that is either to the top, left, right, or bottom ofvalueingrid.int diagonalSum(int value)returns the sum of elements which are diagonal neighbors ofvalue, that is either to the top-left, top-right, bottom-left, or bottom-right ofvalueingrid.
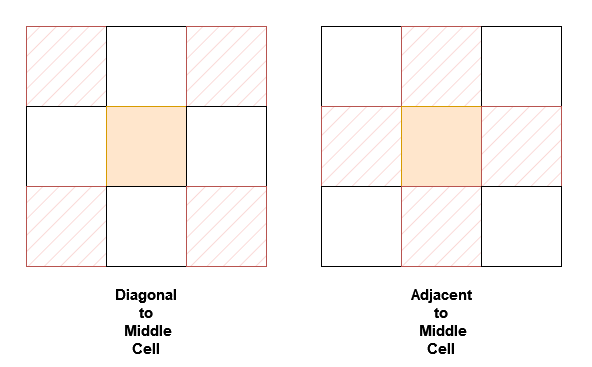
Example 1:
Input:
[“neighborSum”, “adjacentSum”, “adjacentSum”, “diagonalSum”, “diagonalSum”]
[[[[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]], [1], [4], [4], [8]]
Output: [null, 6, 16, 16, 4]
Explanation:
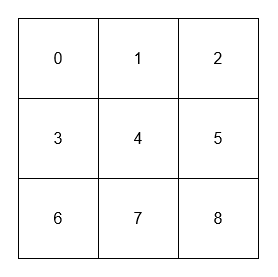
- The adjacent neighbors of 1 are 0, 2, and 4.
- The adjacent neighbors of 4 are 1, 3, 5, and 7.
- The diagonal neighbors of 4 are 0, 2, 6, and 8.
- The diagonal neighbor of 8 is 4.
Example 2:
Input:
[“neighborSum”, “adjacentSum”, “diagonalSum”]
[[[[1, 2, 0, 3], [4, 7, 15, 6], [8, 9, 10, 11], [12, 13, 14, 5]]], [15], [9]]
Output: [null, 23, 45]
Explanation:
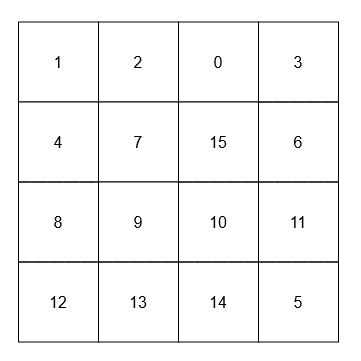
- The adjacent neighbors of 15 are 0, 10, 7, and 6.
- The diagonal neighbors of 9 are 4, 12, 14, and 15.
Constraints:
3 <= n == grid.length == grid[0].length <= 100 <= grid[i][j] <= n2 - 1- All
grid[i][j]are distinct. valueinadjacentSumanddiagonalSumwill be in the range[0, n2 - 1].- At most
2 * n2calls will be made toadjacentSumanddiagonalSum.
Solution
class NeighborSum(private val grid: Array<IntArray>) {
private val n = grid.size
private val rowIndex = IntArray(n * n)
private val colIndex = IntArray(n * n)
init {
// Precompute the positions of each value in the grid for quick access
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
rowIndex[grid[i][j]] = i
colIndex[grid[i][j]] = j
}
}
}
fun adjacentSum(value: Int): Int {
var sum = 0
val i = rowIndex[value]
val j = colIndex[value]
// Check up
if (i > 0) {
sum += grid[i - 1][j]
}
// Check down
if (i < n - 1) {
sum += grid[i + 1][j]
}
// Check left
if (j > 0) {
sum += grid[i][j - 1]
}
// Check right
if (j < n - 1) {
sum += grid[i][j + 1]
}
return sum
}
fun diagonalSum(value: Int): Int {
var sum = 0
val i = rowIndex[value]
val j = colIndex[value]
// Check top-left
if (i > 0 && j > 0) {
sum += grid[i - 1][j - 1]
}
// Check top-right
if (i > 0 && j < n - 1) {
sum += grid[i - 1][j + 1]
}
// Check bottom-left
if (i < n - 1 && j > 0) {
sum += grid[i + 1][j - 1]
}
// Check bottom-right
if (i < n - 1 && j < n - 1) {
sum += grid[i + 1][j + 1]
}
return sum
}
}
/*
* Your neighborSum object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = neighborSum(grid)
* var param_1 = obj.adjacentSum(value)
* var param_2 = obj.diagonalSum(value)
*/

