LeetCode in Kotlin
2718. Sum of Matrix After Queries
Medium
You are given an integer n and a 0-indexed 2D array queries where queries[i] = [typei, indexi, vali].
Initially, there is a 0-indexed n x n matrix filled with 0’s. For each query, you must apply one of the following changes:
- if
typei == 0, set the values in the row withindexitovali, overwriting any previous values. - if
typei == 1, set the values in the column withindexitovali, overwriting any previous values.
Return the sum of integers in the matrix after all queries are applied.
Example 1:
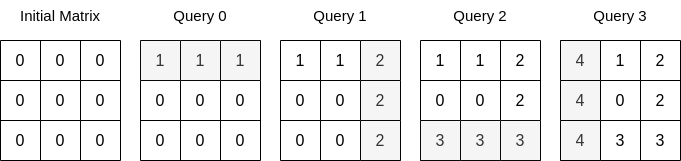
Input: n = 3, queries = [[0,0,1],[1,2,2],[0,2,3],[1,0,4]]
Output: 23
Explanation: The image above describes the matrix after each query. The sum of the matrix after all queries are applied is 23.
Example 2:
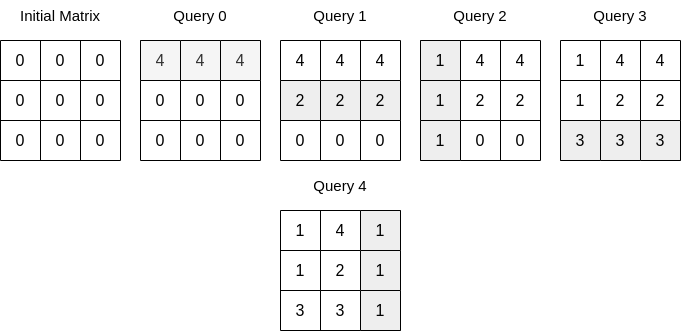
Input: n = 3, queries = [[0,0,4],[0,1,2],[1,0,1],[0,2,3],[1,2,1]]
Output: 17
Explanation: The image above describes the matrix after each query. The sum of the matrix after all queries are applied is 17.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1041 <= queries.length <= 5 * 104queries[i].length == 30 <= typei <= 10 <= indexi < n0 <= vali <= 105
Solution
class Solution {
fun matrixSumQueries(n: Int, queries: Array<IntArray>): Long {
val queriedRow = BooleanArray(n)
val queriedCol = BooleanArray(n)
var sum: Long = 0
var remainingRows = n
var remainingCols = n
for (i in queries.indices.reversed()) {
val type = queries[i][0]
val index = queries[i][1]
val value = queries[i][2]
if (type == 0) {
if (queriedRow[index]) {
continue
}
sum += (value * remainingCols).toLong()
remainingRows--
queriedRow[index] = true
} else {
if (queriedCol[index]) {
continue
}
sum += (value * remainingRows).toLong()
remainingCols--
queriedCol[index] = true
}
}
return sum
}
}

