LeetCode in Kotlin
2642. Design Graph With Shortest Path Calculator
Hard
There is a directed weighted graph that consists of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The edges of the graph are initially represented by the given array edges where edges[i] = [fromi, toi, edgeCosti] meaning that there is an edge from fromi to toi with the cost edgeCosti.
Implement the Graph class:
Graph(int n, int[][] edges)initializes the object withnnodes and the given edges.addEdge(int[] edge)adds an edge to the list of edges whereedge = [from, to, edgeCost]. It is guaranteed that there is no edge between the two nodes before adding this one.int shortestPath(int node1, int node2)returns the minimum cost of a path fromnode1tonode2. If no path exists, return-1. The cost of a path is the sum of the costs of the edges in the path.
Example 1:
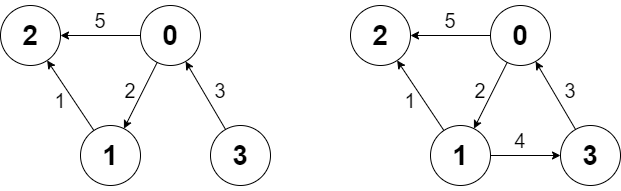
Input [“Graph”, “shortestPath”, “shortestPath”, “addEdge”, “shortestPath”] [[4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]], [3, 2], [0, 3], [[1, 3, 4]], [0, 3]]
Output: [null, 6, -1, null, 6]
Explanation:
Graph g = new Graph(4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]);
g.shortestPath(3, 2); // return 6. The shortest path from 3 to 2 in the first diagram above is 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 with a total cost of 3 + 2 + 1 = 6.
g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return -1. There is no path from 0 to 3.
g.addEdge([1, 3, 4]); // We add an edge from node 1 to node 3, and we get the second diagram above.
g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return 6. The shortest path from 0 to 3 now is 0 -> 1 -> 3 with a total cost of 2 + 4 = 6.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1)edges[i].length == edge.length == 30 <= fromi, toi, from, to, node1, node2 <= n - 11 <= edgeCosti, edgeCost <= 106- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph at any point.
- At most
100calls will be made foraddEdge. - At most
100calls will be made forshortestPath.
Solution
import java.util.PriorityQueue
class Graph(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>) {
private val adj = HashMap<Int, ArrayList<Pair<Int, Int>>>().apply {
for (i in 0 until n)
this[i] = ArrayList<Pair<Int, Int>>()
for ((u, v, cost) in edges) {
this[u] = getOrDefault(u, ArrayList<Pair<Int, Int>>()).apply { this.add(v to cost) }
}
}
fun addEdge(edge: IntArray) {
val (u, v, cost) = edge
adj[u] = adj.getOrDefault(u, ArrayList<Pair<Int, Int>>()).apply { this.add(v to cost) }
}
fun shortestPath(node1: Int, node2: Int): Int {
val minHeap = PriorityQueue<Pair<Int, Int>> { a, b -> a.second - b.second }
val distance = IntArray(adj.size) { Integer.MAX_VALUE }
minHeap.add(node1 to 0)
distance[node1] = 0
while (minHeap.isNotEmpty()) {
val (node, cost) = minHeap.poll()
if (node == node2) return cost
if (cost > distance[node]) continue
adj[node]?.let {
for ((next, nextCost) in adj[node]!!) {
if (cost + nextCost < distance[next]) {
distance[next] = cost + nextCost
minHeap.add(next to cost + nextCost)
}
}
}
}
return -1
}
}
/*
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = Graph(n, edges)
* obj.addEdge(edge)
* var param_2 = obj.shortestPath(node1,node2)
*/

