LeetCode in Kotlin
2617. Minimum Number of Visited Cells in a Grid
Hard
You are given a 0-indexed m x n integer matrix grid. Your initial position is at the top-left cell (0, 0).
Starting from the cell (i, j), you can move to one of the following cells:
- Cells
(i, k)withj < k <= grid[i][j] + j(rightward movement), or - Cells
(k, j)withi < k <= grid[i][j] + i(downward movement).
Return the minimum number of cells you need to visit to reach the bottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1). If there is no valid path, return -1.
Example 1:
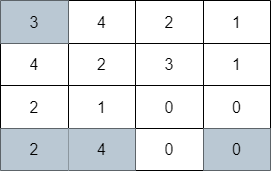
Input: grid = [[3,4,2,1],[4,2,3,1],[2,1,0,0],[2,4,0,0]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The image above shows one of the paths that visits exactly 4 cells.
Example 2:
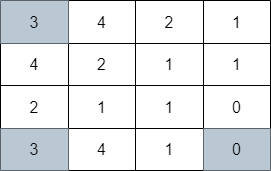
Input: grid = [[3,4,2,1],[4,2,1,1],[2,1,1,0],[3,4,1,0]]
Output: 3
Explanation: The image above shows one of the paths that visits exactly 3 cells.
Example 3:
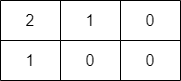
Input: grid = [[2,1,0],[1,0,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: It can be proven that no path exists.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 1050 <= grid[i][j] < m * ngrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 0
Solution
import java.util.LinkedList
import java.util.Queue
class Solution {
fun minimumVisitedCells(grid: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val len = Array(grid.size) { IntArray(grid[0].size) }
for (ints in len) {
ints.fill(-1)
}
val q: Queue<IntArray> = LinkedList()
q.add(intArrayOf(0, 0))
len[0][0] = 1
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val tmp = q.poll()
val i = tmp[0]
val j = tmp[1]
var c = 0
for (k in Math.min(grid[0].size - 1, grid[i][j] + j) downTo j + 1) {
if (len[i][k] != -1) {
c++
if (c > LIMIT) {
break
}
} else {
len[i][k] = len[i][j] + 1
q.add(intArrayOf(i, k))
}
}
if (len[grid.size - 1][grid[0].size - 1] != -1) {
return len[grid.size - 1][grid[0].size - 1]
}
c = 0
for (k in Math.min(grid.size - 1, grid[i][j] + i) downTo i + 1) {
if (len[k][j] != -1) {
c++
if (c > LIMIT) {
break
}
} else {
len[k][j] = len[i][j] + 1
q.add(intArrayOf(k, j))
}
}
if (len[grid.size - 1][grid[0].size - 1] != -1) {
return len[grid.size - 1][grid[0].size - 1]
}
}
return -1
}
companion object {
private const val LIMIT = 2
}
}

