LeetCode in Kotlin
2583. Kth Largest Sum in a Binary Tree
Medium
You are given the root of a binary tree and a positive integer k.
The level sum in the tree is the sum of the values of the nodes that are on the same level.
Return the kth largest level sum in the tree (not necessarily distinct). If there are fewer than k levels in the tree, return -1.
Note that two nodes are on the same level if they have the same distance from the root.
Example 1:

Input: root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], k = 2
Output: 13
Explanation: The level sums are the following:
-
Level 1: 5. - Level 2: 8 + 9 = 17.
-
Level 3: 2 + 1 + 3 + 7 = 13.
-
Level 4: 4 + 6 = 10. The 2nd largest level sum is 13.
Example 2:
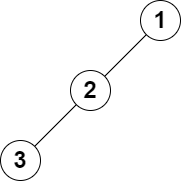
Input: root = [1,2,null,3], k = 1
Output: 3
Explanation: The largest level sum is 3.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= 1061 <= k <= n
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
import java.util.LinkedList
import java.util.PriorityQueue
import java.util.Queue
class Solution {
fun kthLargestLevelSum(root: TreeNode?, k: Int): Long {
val heap: Queue<Long> = PriorityQueue()
val levels: Queue<TreeNode?> = LinkedList()
levels.offer(root)
while (levels.isNotEmpty()) {
var sum: Long = 0
val size: Int = levels.size
for (i in 0 until size) {
val node = levels.poll()
sum += node!!.`val`
if (node.left != null) levels.offer(node.left)
if (node.right != null) levels.offer(node.right)
}
if (heap.size < k) {
heap.offer(sum)
} else if (heap.peek() < sum) {
heap.poll()
heap.offer(sum)
}
}
return if (heap.size < k) -1 else heap.peek()
}
}

