LeetCode in Kotlin
2471. Minimum Number of Operations to Sort a Binary Tree by Level
Medium
You are given the root of a binary tree with unique values.
In one operation, you can choose any two nodes at the same level and swap their values.
Return the minimum number of operations needed to make the values at each level sorted in a strictly increasing order.
The level of a node is the number of edges along the path between it and the root node_._
Example 1:
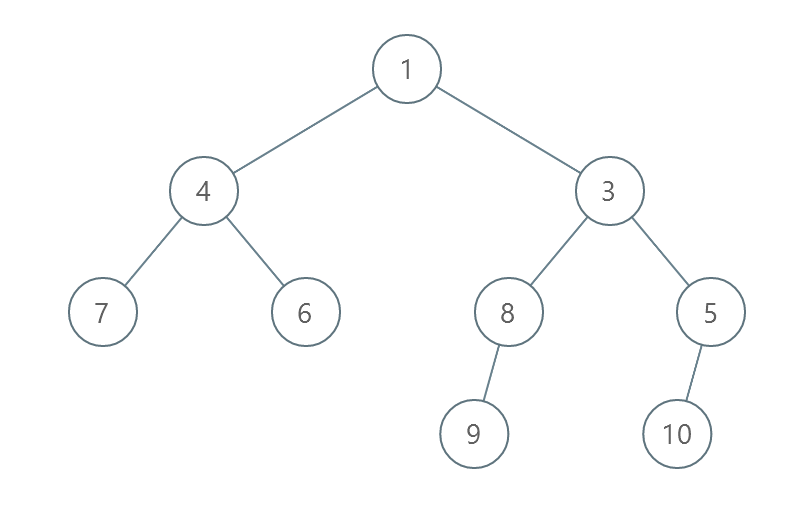
Input: root = [1,4,3,7,6,8,5,null,null,null,null,9,null,10]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- Swap 4 and 3. The 2nd level becomes [3,4].
- Swap 7 and 5. The 3rd level becomes [5,6,8,7].
- Swap 8 and 7. The 3rd level becomes [5,6,7,8].
We used 3 operations so return 3. It can be proven that 3 is the minimum number of operations needed.
Example 2:
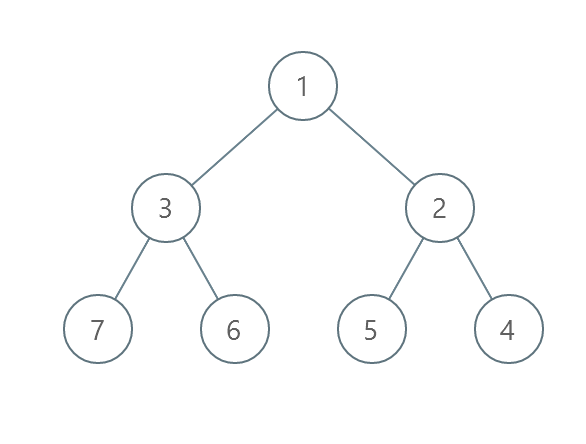
Input: root = [1,3,2,7,6,5,4]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- Swap 3 and 2. The 2nd level becomes [2,3].
- Swap 7 and 4. The 3rd level becomes [4,6,5,7].
- Swap 6 and 5. The 3rd level becomes [4,5,6,7].
We used 3 operations so return 3. It can be proven that 3 is the minimum number of operations needed.
Example 3:
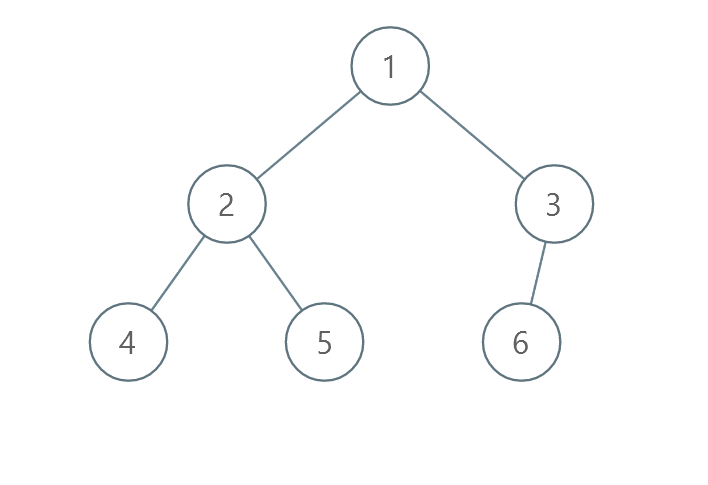
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: 0
Explanation: Each level is already sorted in increasing order so return 0.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- All the values of the tree are unique.
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
import java.util.ArrayDeque
/*
* Example:
* var ti = TreeNode(5)
* var v = ti.`val`
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var left: TreeNode? = null
* var right: TreeNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun minimumOperations(root: TreeNode): Int {
val q = ArrayDeque<TreeNode>()
var count = 0
if (root.left != null && root.right != null && root.left!!.`val` > root.right!!.`val`) {
count++
}
if (root.left != null) {
q.add(root.left)
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.add(root.right)
}
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
var size = q.size
val al: MutableList<Int> = ArrayList()
while (size-- > 0) {
val node = q.poll()!!
if (node.left != null) {
al.add(node.left!!.`val`)
q.add(node.left)
}
if (node.right != null) {
al.add(node.right!!.`val`)
q.add(node.right)
}
}
count += helper(al)
}
return count
}
private fun helper(list: MutableList<Int>): Int {
var swaps = 0
val sorted = IntArray(list.size)
for (i in sorted.indices) {
sorted[i] = list[i]
}
sorted.sort()
val ind: MutableMap<Int, Int> = HashMap()
for (i in list.indices) {
ind[list[i]] = i
}
for (i in list.indices) {
if (list[i] != sorted[i]) {
swaps++
ind[list[i]] = ind[sorted[i]]!!
list[ind[sorted[i]]!!] = list[i]
}
}
return swaps
}
}

