LeetCode in Kotlin
2003. Smallest Missing Genetic Value in Each Subtree
Hard
There is a family tree rooted at 0 consisting of n nodes numbered 0 to n - 1. You are given a 0-indexed integer array parents, where parents[i] is the parent for node i. Since node 0 is the root, parents[0] == -1.
There are 105 genetic values, each represented by an integer in the inclusive range [1, 105]. You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums, where nums[i] is a distinct genetic value for node i.
Return an array ans of length n where ans[i] is the smallest genetic value that is missing from the subtree rooted at node i.
The subtree rooted at a node x contains node x and all of its descendant nodes.
Example 1:
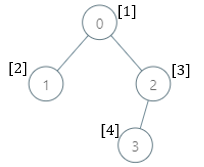
Input: parents = [-1,0,0,2], nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [5,1,1,1]
Explanation: The answer for each subtree is calculated as follows:
-
0: The subtree contains nodes [0,1,2,3] with values [1,2,3,4]. 5 is the smallest missing value.
-
1: The subtree contains only node 1 with value 2. 1 is the smallest missing value.
-
2: The subtree contains nodes [2,3] with values [3,4]. 1 is the smallest missing value.
-
3: The subtree contains only node 3 with value 4. 1 is the smallest missing value.
Example 2:
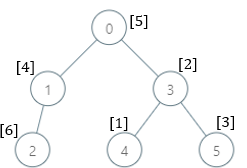
Input: parents = [-1,0,1,0,3,3], nums = [5,4,6,2,1,3]
Output: [7,1,1,4,2,1]
Explanation: The answer for each subtree is calculated as follows:
-
0: The subtree contains nodes [0,1,2,3,4,5] with values [5,4,6,2,1,3]. 7 is the smallest missing value.
-
1: The subtree contains nodes [1,2] with values [4,6]. 1 is the smallest missing value.
-
2: The subtree contains only node 2 with value 6. 1 is the smallest missing value.
-
3: The subtree contains nodes [3,4,5] with values [2,1,3]. 4 is the smallest missing value.
-
4: The subtree contains only node 4 with value 1. 2 is the smallest missing value.
-
5: The subtree contains only node 5 with value 3. 1 is the smallest missing value.
Example 3:
Input: parents = [-1,2,3,0,2,4,1], nums = [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
Output: [1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
Explanation: The value 1 is missing from all the subtrees.
Constraints:
n == parents.length == nums.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= parents[i] <= n - 1fori != 0parents[0] == -1parentsrepresents a valid tree.1 <= nums[i] <= 105- Each
nums[i]is distinct.
Solution
@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
class Solution {
fun smallestMissingValueSubtree(parents: IntArray, nums: IntArray): IntArray {
val ans = IntArray(parents.size)
val all = arrayOfNulls<Node>(parents.size)
var max = 0
for (i in nums.indices) {
all[i] = Node(i, nums[i])
max = max.coerceAtLeast(nums[i])
}
for (i in 1 until parents.size) {
all[parents[i]]!!.nodes.add(all[i])
}
solve(all[0], ans, UF(++max, nums))
return ans
}
private fun solve(root: Node?, ans: IntArray, uf: UF) {
var max = 1
for (child in root!!.nodes) {
solve(child, ans, uf)
uf.union(root.`val`, child!!.`val`)
max = ans[child.idx].coerceAtLeast(max)
}
while (max <= ans.size && uf.isConnected(max, root.`val`)) {
++max
}
ans[root.idx] = max
}
private class Node internal constructor(var idx: Int, var `val`: Int) {
var nodes: MutableList<Node?> = ArrayList()
}
private class UF internal constructor(n: Int, nums: IntArray) {
var rank: IntArray
var parent: IntArray
init {
rank = IntArray(n)
parent = IntArray(n)
for (m in nums) {
parent[m] = m
}
}
private fun find(x: Int): Int {
if (x == parent[x]) {
return x
}
parent[x] = find(parent[x])
return parent[x]
}
fun union(x: Int, y: Int) {
var x = x
var y = y
x = find(x)
y = find(y)
if (rank[x] > rank[y]) {
parent[y] = x
} else {
parent[x] = y
if (rank[x] == rank[y]) {
rank[y]++
}
}
}
fun isConnected(x: Int, y: Int): Boolean {
return find(x) == find(y)
}
}
}

