LeetCode in Kotlin
1719. Number Of Ways To Reconstruct A Tree
Hard
You are given an array pairs, where pairs[i] = [xi, yi], and:
- There are no duplicates.
xi < yi
Let ways be the number of rooted trees that satisfy the following conditions:
- The tree consists of nodes whose values appeared in
pairs. - A pair
[xi, yi]exists inpairsif and only ifxiis an ancestor ofyioryiis an ancestor ofxi. - Note: the tree does not have to be a binary tree.
Two ways are considered to be different if there is at least one node that has different parents in both ways.
Return:
0ifways == 01ifways == 12ifways > 1
A rooted tree is a tree that has a single root node, and all edges are oriented to be outgoing from the root.
An ancestor of a node is any node on the path from the root to that node (excluding the node itself). The root has no ancestors.
Example 1:
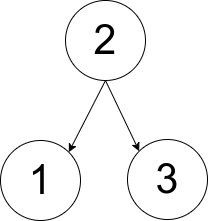
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3]]
Output: 1
Explanation: There is exactly one valid rooted tree, which is shown in the above figure.
Example 2:
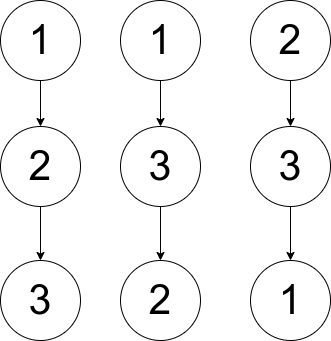
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3],[1,3]]
Output: 2
Explanation: There are multiple valid rooted trees. Three of them are shown in the above figures.
Example 3:
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3],[2,4],[1,5]]
Output: 0
Explanation: There are no valid rooted trees.
Constraints:
1 <= pairs.length <= 1051 <= xi < yi <= 500- The elements in
pairsare unique.
Solution
class Solution {
fun checkWays(pairs: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val adj = Array(501) { IntArray(501) }
val set = HashSet<Int>()
for (pair in pairs) {
adj[pair[0]][pair[1]]++
adj[pair[1]][pair[0]]++
set.add(pair[0])
set.add(pair[1])
}
val n = set.size
val num = IntArray(501)
for (i in 0..500) {
for (j in 0..500) {
num[i] += adj[i][j]
}
}
var c = 0
for (i in 0..500) {
if (num[i] == n - 1) {
c++
}
}
for (j in 0..500) {
if (num[j] == n - 1) {
num[j] = 0
for (k in 0..500) {
if (adj[j][k] > 0) {
adj[j][k] = 0
adj[k][j] = 0
num[k]--
}
}
set.remove(j)
break
}
if (j == 500) {
return 0
}
}
val res = search(adj, num, set)
return if (res == 1 && c > 1) {
2
} else {
res
}
}
private fun search(adj: Array<IntArray>, num: IntArray, vals: HashSet<Int>): Int {
if (vals.isEmpty()) {
return 1
}
var max = 0
for (i in vals) {
if (num[i] > num[max]) {
max = i
}
}
val size = num[max]
if (size == 0) {
return 1
}
var c = false
i@ for (i in vals) {
if (num[i] == num[max]) {
for (j in vals) {
if (j != i && num[j] == num[i] && adj[i][j] > 0) {
c = true
break@i
}
}
}
}
val set = HashSet<Int>()
for (j in 0..500) {
if (adj[max][j] > 0 && !vals.contains(j)) {
return 0
}
if (adj[max][j] > 0) {
adj[max][j] = 0
adj[j][max] = 0
num[j]--
set.add(j)
}
}
num[max] = 0
val set2 = HashSet<Int>()
for (i in vals) {
if (!set.contains(i) && i != max) {
set2.add(i)
}
}
val res1 = search(adj, num, set)
val res2 = search(adj, num, set2)
if (res1 == 0 || res2 == 0) {
return 0
}
return if (res1 == 2 || res2 == 2 || c) {
2
} else {
1
}
}
}

