LeetCode in Kotlin
1489. Find Critical and Pseudo-Critical Edges in Minimum Spanning Tree
Hard
Given a weighted undirected connected graph with n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between nodes ai and bi. A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a subset of the graph’s edges that connects all vertices without cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
Find all the critical and pseudo-critical edges in the given graph’s minimum spanning tree (MST). An MST edge whose deletion from the graph would cause the MST weight to increase is called a critical edge. On the other hand, a pseudo-critical edge is that which can appear in some MSTs but not all.
Note that you can return the indices of the edges in any order.
Example 1:
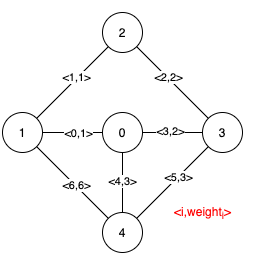
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,2],[0,3,2],[0,4,3],[3,4,3],[1,4,6]]
Output: [[0,1],[2,3,4,5]]
Explanation: The figure above describes the graph.
The following figure shows all the possible MSTs:
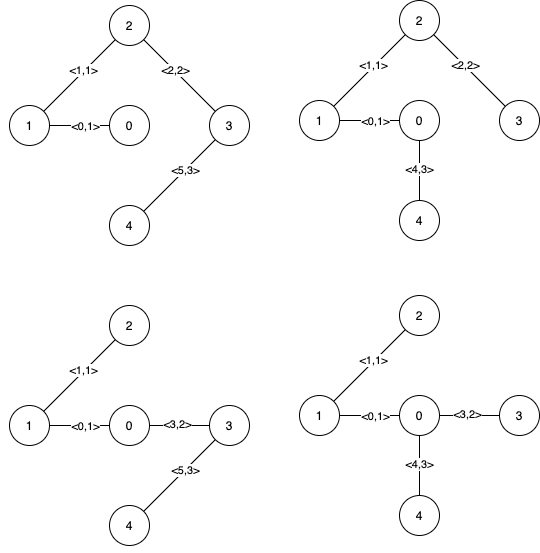
Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output.
The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.
Example 2:
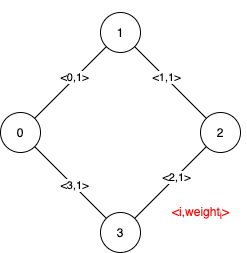
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[0,3,1]]
Output: [[],[0,1,2,3]]
Explanation: We can observe that since all 4 edges have equal weight, choosing any 3 edges from the given 4 will yield an MST. Therefore all 4 edges are pseudo-critical.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= min(200, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 30 <= ai < bi < n1 <= weighti <= 1000- All pairs
(ai, bi)are distinct.
Solution
import java.util.LinkedList
class Solution {
fun findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>): List<List<Int>> {
// {w, ind}
val g = Array(n) { Array(n) { IntArray(2) } }
for (i in edges.indices) {
val e = edges[i]
val f = e[0]
val t = e[1]
val w = e[2]
g[f][t][0] = w
g[t][f][0] = w
g[f][t][1] = i
g[t][f][1] = i
}
val mst: Array<MutableList<Int>?> = arrayOfNulls(n)
for (i in 0 until n) {
mst[i] = LinkedList()
}
val mstSet = BooleanArray(edges.size)
edges.sortWith { a: IntArray, b: IntArray ->
Integer.compare(
a[2],
b[2],
)
}
buildMST(n, edges, mstSet, mst, g)
val ans: MutableList<List<Int>> = ArrayList(2)
val pce: MutableSet<Int> = HashSet()
val ce: MutableList<Int> = LinkedList()
// pseudo critical edges
for (edge in edges) {
val f = edge[0]
val t = edge[1]
val w = edge[2]
val ind = g[f][t][1]
if (!mstSet[ind]) {
val cur: MutableSet<Int> = HashSet()
val p = path(f, t, w, -1, mst, g, cur)
if (p && cur.isNotEmpty()) {
pce.addAll(cur)
pce.add(ind)
}
if (!p) {
println("Should not reach here")
}
}
}
// critical edges
for (edge in edges) {
val f = edge[0]
val t = edge[1]
val ind = g[f][t][1]
if (mstSet[ind] && !pce.contains(ind)) {
ce.add(ind)
}
}
ans.add(ce)
ans.add(LinkedList(pce))
return ans
}
private fun path(
f: Int,
t: Int,
w: Int,
p: Int,
mst: Array<MutableList<Int>?>,
g: Array<Array<IntArray>>,
ind: MutableSet<Int>,
): Boolean {
if (f == t) {
return true
}
for (nbr in mst[f]!!) {
if (p != nbr && path(nbr, t, w, f, mst, g, ind)) {
if (g[f][nbr][0] == w) {
ind.add(g[f][nbr][1])
}
return true
}
}
return false
}
private fun buildMST(
n: Int,
edges: Array<IntArray>,
mste: BooleanArray,
mstg: Array<MutableList<Int>?>,
g: Array<Array<IntArray>>,
) {
val ds = DisjointSet(n)
for (ints in edges) {
if (ds.union(ints[0], ints[1])) {
mstg[ints[0]]?.add(ints[1])
mstg[ints[1]]?.add(ints[0])
mste[g[ints[0]][ints[1]][1]] = true
}
}
}
private class DisjointSet(n: Int) {
var parent: IntArray
init {
parent = IntArray(n)
for (i in 0 until n) {
parent[i] = i
}
}
fun find(i: Int): Int {
if (i == parent[i]) {
return i
}
parent[i] = find(parent[i])
return parent[i]
}
fun union(u: Int, v: Int): Boolean {
val pu = find(u)
val pv = find(v)
if (pu == pv) {
return false
}
parent[pu] = pv
return true
}
}
}

