LeetCode in Kotlin
1260. Shift 2D Grid
Easy
Given a 2D grid of size m x n and an integer k. You need to shift the grid k times.
In one shift operation:
- Element at
grid[i][j]moves togrid[i][j + 1]. - Element at
grid[i][n - 1]moves togrid[i + 1][0]. - Element at
grid[m - 1][n - 1]moves togrid[0][0].
Return the 2D grid after applying shift operation k times.
Example 1:
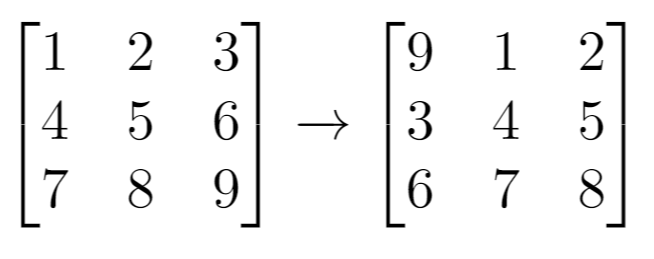
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 1
Output: [[9,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]
Example 2:
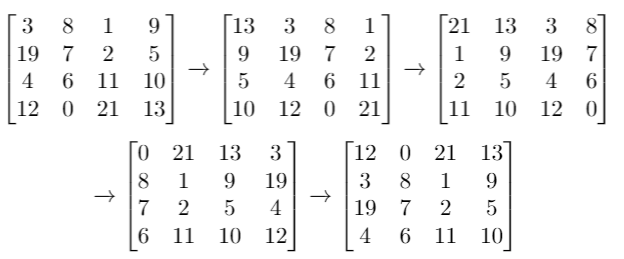
Input: grid = [[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10],[12,0,21,13]], k = 4
Output: [[12,0,21,13],[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10]]
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 9
Output: [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m <= 501 <= n <= 50-1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 10000 <= k <= 100
Solution
class Solution {
fun shiftGrid(grid: Array<IntArray>, k: Int): List<List<Int>> {
val flat = IntArray(grid.size * grid[0].size)
var index = 0
for (ints in grid) {
for (j in grid[0].indices) {
flat[index++] = ints[j]
}
}
val mode = k % flat.size
var readingIndex = flat.size - mode
if (readingIndex == flat.size) {
readingIndex = 0
}
val result: MutableList<List<Int>> = ArrayList()
for (i in grid.indices) {
val eachRow: MutableList<Int> = ArrayList()
for (j in grid[0].indices) {
eachRow.add(flat[readingIndex++])
if (readingIndex == flat.size) {
readingIndex = 0
}
}
result.add(eachRow)
}
return result
}
}

