LeetCode in Kotlin
1123. Lowest Common Ancestor of Deepest Leaves
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, return the lowest common ancestor of its deepest leaves.
Recall that:
- The node of a binary tree is a leaf if and only if it has no children
- The depth of the root of the tree is
0. if the depth of a node isd, the depth of each of its children isd + 1. - The lowest common ancestor of a set
Sof nodes, is the nodeAwith the largest depth such that every node inSis in the subtree with rootA.
Example 1:
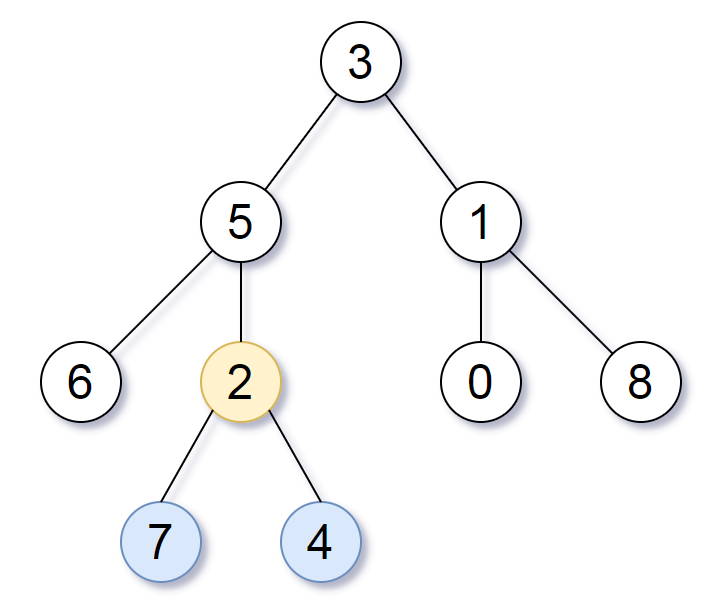
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
Output: [2,7,4]
Explanation: We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram. The nodes coloured in blue are the deepest leaf-nodes of the tree. Note that nodes 6, 0, and 8 are also leaf nodes, but the depth of them is 2, but the depth of nodes 7 and 4 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Explanation: The root is the deepest node in the tree, and it’s the lca of itself.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2]
Output: [2]
Explanation: The deepest leaf node in the tree is 2, the lca of one node is itself.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
Note: This question is the same as 865: https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
/*
* Example:
* var ti = TreeNode(5)
* var v = ti.`val`
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var left: TreeNode? = null
* var right: TreeNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun lcaDeepestLeaves(root: TreeNode?): TreeNode? {
if (root == null) {
return null
}
val leftDep = getDep(root.left)
val rightDep = getDep(root.right)
return if (leftDep == rightDep) {
root
} else {
if (leftDep > rightDep) {
lcaDeepestLeaves(root.left)
} else {
lcaDeepestLeaves(root.right)
}
}
}
fun getDep(root: TreeNode?): Int {
return if (root == null) {
0
} else {
1 + Math.max(getDep(root.left), getDep(root.right))
}
}
}

