LeetCode in Kotlin
1039. Minimum Score Triangulation of Polygon
Medium
You have a convex n-sided polygon where each vertex has an integer value. You are given an integer array values where values[i] is the value of the ith vertex (i.e., clockwise order).
You will triangulate the polygon into n - 2 triangles. For each triangle, the value of that triangle is the product of the values of its vertices, and the total score of the triangulation is the sum of these values over all n - 2 triangles in the triangulation.
Return the smallest possible total score that you can achieve with some triangulation of the polygon.
Example 1:
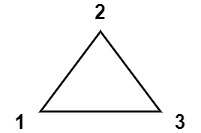
Input: values = [1,2,3]
Output: 6
Explanation: The polygon is already triangulated, and the score of the only triangle is 6.
Example 2:
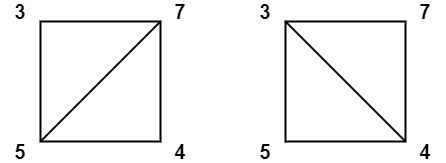
Input: values = [3,7,4,5]
Output: 144
Explanation: There are two triangulations, with possible scores: 3*7*5 + 4*5*7 = 245, or 3*4*5 + 3*4*7 = 144. The minimum score is 144.
Example 3:
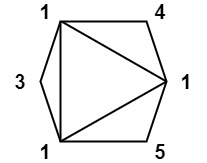
Input: values = [1,3,1,4,1,5]
Output: 13
Explanation: The minimum score triangulation has score 1*1*3 + 1*1*4 + 1*1*5 + 1*1*1 = 13.
Constraints:
n == values.length3 <= n <= 501 <= values[i] <= 100
Solution
class Solution {
private val dp = Array(101) { IntArray(101) }
fun minScoreTriangulation(values: IntArray): Int {
val n = values.size
for (row: IntArray? in dp) {
row!!.fill(-1)
}
return util(values, 1, n - 1)
}
private fun util(values: IntArray, i: Int, j: Int): Int {
if (i >= j) {
return 0
}
if (dp[i][j] != -1) {
return dp[i][j]
}
var ans = Int.MAX_VALUE
for (k in i until j) {
val temp = (
util(values, i, k) +
util(values, k + 1, j) +
(values[i - 1] * values[k] * values[j])
)
ans = ans.coerceAtMost(temp)
dp[i][j] = ans
}
return dp[i][j]
}
}

