LeetCode in Kotlin
894. All Possible Full Binary Trees
Medium
Given an integer n, return a list of all possible full binary trees with n nodes. Each node of each tree in the answer must have Node.val == 0.
Each element of the answer is the root node of one possible tree. You may return the final list of trees in any order.
A full binary tree is a binary tree where each node has exactly 0 or 2 children.
Example 1:
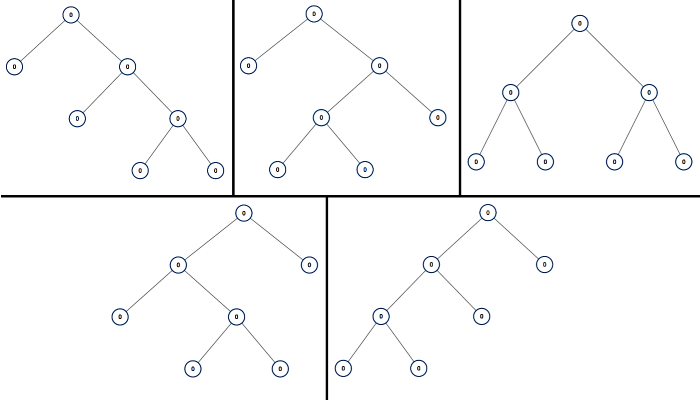
Input: n = 7
Output: [[0,0,0,null,null,0,0,null,null,0,0],[0,0,0,null,null,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,null,null,null,null,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,null,null,0,0]]
Example 2:
Input: n = 3
Output: [[0,0,0]]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 20
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
/*
* Example:
* var ti = TreeNode(5)
* var v = ti.`val`
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var left: TreeNode? = null
* var right: TreeNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun allPossibleFBT(n: Int): List<TreeNode> {
if (n % 2 == 0) {
// no complete binary tree possible
return ArrayList()
}
val dp: Array<ArrayList<TreeNode>?> = arrayOfNulls(n + 1)
// form left to right
var i = 1
while (i <= n) {
helper(i, dp)
i += 2
}
return dp[n]!!
}
// Using tabulation
private fun helper(n: Int, dp: Array<ArrayList<TreeNode>?>) {
if (n <= 0) {
return
}
if (n == 1) {
dp[1] = ArrayList()
dp[1]!!.add(TreeNode(0))
return
}
dp[n] = ArrayList()
var i = 1
while (i < n) {
// left
for (nodeL in dp[i]!!) {
// right
for (nodeR in dp[n - i - 1]!!) {
// 1 node used here
val root = TreeNode(0)
root.left = nodeL
root.right = nodeR
dp[n]!!.add(root)
}
}
i += 2
}
}
}

