LeetCode in Kotlin
863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, the value of a target node target, and an integer k, return an array of the values of all nodes that have a distance k from the target node.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
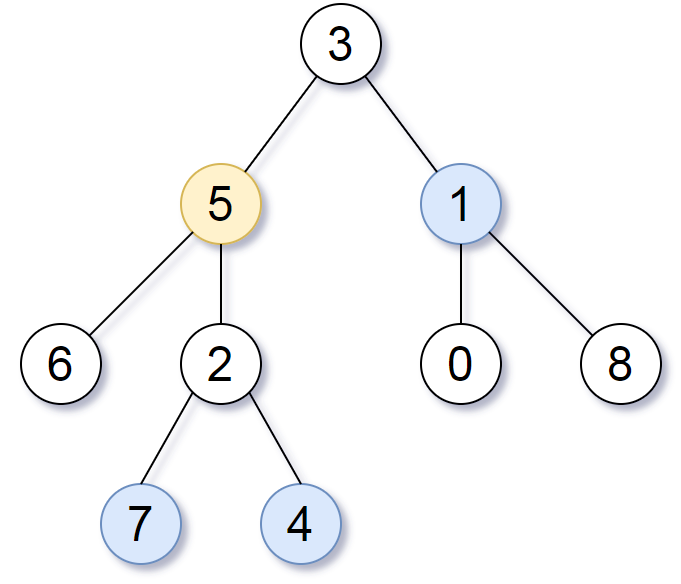
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, k = 2
Output: [7,4,1] Explanation: The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5) have values 7, 4, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 1, k = 3
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- All the values
Node.valare unique. targetis the value of one of the nodes in the tree.0 <= k <= 1000
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode(var `val`: Int = 0) {
* var left: TreeNode? = null
* var right: TreeNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
private fun kFar(root: TreeNode?, k: Int, visited: TreeNode?, ls: MutableList<Int>) {
if (root == null || k < 0 || root === visited) {
return
}
if (k == 0) {
ls.add(root.`val`)
return
}
kFar(root.left, k - 1, visited, ls)
kFar(root.right, k - 1, visited, ls)
}
fun distanceK(root: TreeNode?, target: TreeNode?, k: Int): List<Int> {
val ls: MutableList<Int> = ArrayList()
if (k == 0) {
ls.add(target!!.`val`)
return ls
}
nodeToRoot(root, target!!, k, ls)
return ls
}
private fun nodeToRoot(root: TreeNode?, target: TreeNode, k: Int, ls: MutableList<Int>): Int {
if (root == null) {
return -1
}
if (root.`val` == target.`val`) {
kFar(root, k, null, ls)
return 1
}
val ld = nodeToRoot(root.left, target, k, ls)
if (ld != -1) {
kFar(root, k - ld, root.left, ls)
return ld + 1
}
val rd = nodeToRoot(root.right, target, k, ls)
if (rd != -1) {
kFar(root, k - rd, root.right, ls)
return rd + 1
}
return -1
}
}

