LeetCode in Kotlin
835. Image Overlap
Medium
You are given two images, img1 and img2, represented as binary, square matrices of size n x n. A binary matrix has only 0s and 1s as values.
We translate one image however we choose by sliding all the 1 bits left, right, up, and/or down any number of units. We then place it on top of the other image. We can then calculate the overlap by counting the number of positions that have a 1 in both images.
Note also that a translation does not include any kind of rotation. Any 1 bits that are translated outside of the matrix borders are erased.
Return the largest possible overlap.
Example 1:
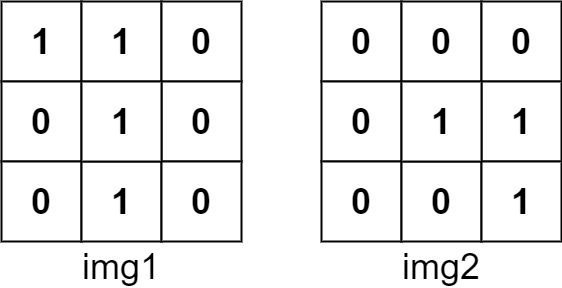
Input: img1 = [[1,1,0],[0,1,0],[0,1,0]], img2 = [[0,0,0],[0,1,1],[0,0,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation: We translate img1 to right by 1 unit and down by 1 unit. 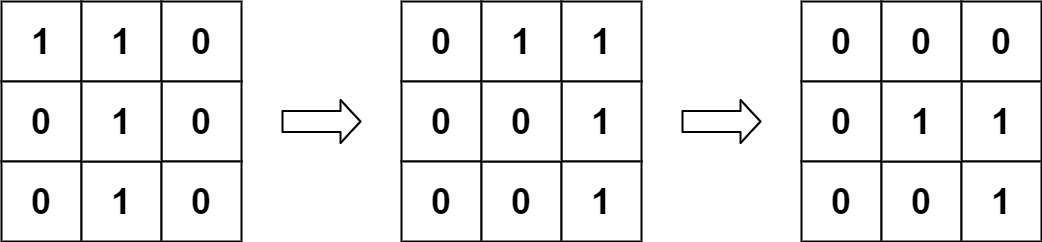 The number of positions that have a 1 in both images is 3 (shown in red).
The number of positions that have a 1 in both images is 3 (shown in red). 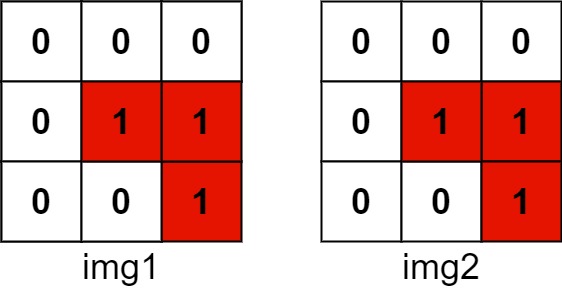
Example 2:
Input: img1 = [[1]], img2 = [[1]]
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: img1 = [[0]], img2 = [[0]]
Output: 0
Constraints:
n == img1.length == img1[i].lengthn == img2.length == img2[i].length1 <= n <= 30img1[i][j]is either0or1.img2[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution
class Solution {
fun largestOverlap(img1: Array<IntArray>, img2: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val bits1 = bitwise(img1)
val bits2 = bitwise(img2)
val n = img1.size
var res = 0
for (hori in -1 * n + 1 until n) {
for (veti in -1 * n + 1 until n) {
var curOverLapping = 0
if (veti < 0) {
for (i in -1 * veti until n) {
curOverLapping += if (hori < 0) {
Integer.bitCount(
bits1[i] shl -1 * hori and bits2[i - -1 * veti],
)
} else {
Integer.bitCount(bits1[i] shr hori and bits2[i - -1 * veti])
}
}
} else {
for (i in 0 until n - veti) {
curOverLapping += if (hori < 0) {
Integer.bitCount(bits1[i] shl -1 * hori and bits2[veti + i])
} else {
Integer.bitCount(bits1[i] shr hori and bits2[veti + i])
}
}
}
res = Math.max(res, curOverLapping)
}
}
return res
}
private fun bitwise(img: Array<IntArray>): IntArray {
val bits = IntArray(img.size)
for (i in img.indices) {
var cur = 0
for (j in img[0].indices) {
cur = cur * 2 + img[i][j]
}
bits[i] = cur
}
return bits
}
}

