LeetCode in Kotlin
764. Largest Plus Sign
Medium
You are given an integer n. You have an n x n binary grid grid with all values initially 1’s except for some indices given in the array mines. The ith element of the array mines is defined as mines[i] = [xi, yi] where grid[xi][yi] == 0.
Return the order of the largest axis-aligned plus sign of 1’s contained in grid. If there is none, return 0.
An axis-aligned plus sign of 1’s of order k has some center grid[r][c] == 1 along with four arms of length k - 1 going up, down, left, and right, and made of 1’s. Note that there could be 0’s or 1’s beyond the arms of the plus sign, only the relevant area of the plus sign is checked for 1’s.
Example 1:
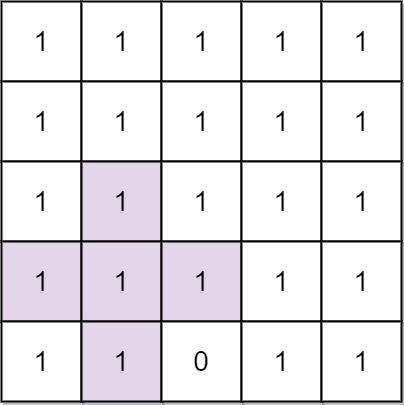
Input: n = 5, mines = [[4,2]]
Output: 2
Explanation: In the above grid, the largest plus sign can only be of order 2. One of them is shown.
Example 2:

Input: n = 1, mines = [[0,0]]
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no plus sign, so return 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5001 <= mines.length <= 50000 <= xi, yi < n- All the pairs
(xi, yi)are unique.
Solution
class Solution {
fun orderOfLargestPlusSign(n: Int, mines: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val mat = Array(n) { BooleanArray(n) }
for (pos in mines) {
mat[pos[0]][pos[1]] = true
}
val left = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
val right = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
val up = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
val down = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
var ans = 0
// For Left and Up only
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
val i1 = if (j == 0) 0 else left[i][j - 1]
left[i][j] = if (mat[i][j]) 0 else 1 + i1
val i2 = if (i == 0) 0 else up[i - 1][j]
up[i][j] = if (mat[i][j]) 0 else 1 + i2
}
}
// For Right and Down and simoultaneously get answer
for (i in n - 1 downTo 0) {
for (j in n - 1 downTo 0) {
val i1 = if (j == n - 1) 0 else right[i][j + 1]
right[i][j] = if (mat[i][j]) 0 else 1 + i1
val i2 = if (i == n - 1) 0 else down[i + 1][j]
down[i][j] = if (mat[i][j]) 0 else 1 + i2
val x = left[i][j].coerceAtMost(up[i][j]).coerceAtMost(
right[i][j].coerceAtMost(down[i][j]),
)
ans = ans.coerceAtLeast(x)
}
}
return ans
}
}

