LeetCode in Kotlin
257. Binary Tree Paths
Easy
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
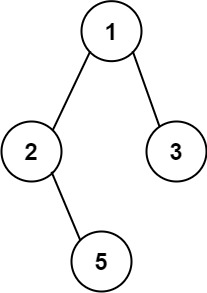
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5]
Output: [“1->2->5”,”1->3”]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [“1”]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
/*
* Example:
* var ti = TreeNode(5)
* var v = ti.`val`
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var left: TreeNode? = null
* var right: TreeNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
private var result: MutableList<String>? = null
private var sb: StringBuilder? = null
fun binaryTreePaths(root: TreeNode?): List<String> {
result = ArrayList()
if (root == null) {
return result as ArrayList<String>
}
sb = StringBuilder()
walkThrough(root)
return result as ArrayList<String>
}
private fun walkThrough(root: TreeNode?) {
assert(root != null)
var length = sb!!.length
sb!!.append(root!!.`val`)
length = sb!!.length - length
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// leaf node.
result!!.add(sb.toString())
sb!!.delete(sb!!.length - length, sb!!.length)
return
}
sb!!.append("->")
length += 2
if (root.left != null) {
walkThrough(root.left)
}
if (root.right != null) {
walkThrough(root.right)
}
sb!!.delete(sb!!.length - length, sb!!.length)
}
}

